How to Target a Microbial Needle within a Community Haystack
A team developed a pipeline to first target cells from uncultivated microbes, and then retrieve and characterize their genomes. [Read More]
 A team developed a pipeline to first target cells from uncultivated microbes, and then retrieve and characterize their genomes. [Read More]
A team developed a pipeline to first target cells from uncultivated microbes, and then retrieve and characterize their genomes. [Read More] Understanding the mechanisms by which potential biofuel feedstocks reproduce can help guide breeding efforts. [Read More]
Understanding the mechanisms by which potential biofuel feedstocks reproduce can help guide breeding efforts. [Read More] A team led by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley used a multi-omics approach to reconstruct and model gene regulatory pathways used by the filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa, and to identify and decide on the order in which this fungus breaks down plant cell wall materials including lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose. [Read More]
A team led by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley used a multi-omics approach to reconstruct and model gene regulatory pathways used by the filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa, and to identify and decide on the order in which this fungus breaks down plant cell wall materials including lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose. [Read More]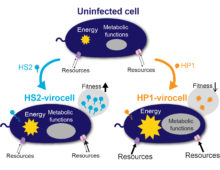 If it looks like a duck and quacks like a duck, so the adage goes, it must be a duck. But if the duck gets infected by a virus so that it no longer looks or quacks like one, is it still a duck? For a team led by researchers from The Ohio State University and the University of Michigan studying how virus infections cause significant metabolic changes in marine microbes, the answer is no. They refer to the infected microbial cells as virocells, a change in name which reflects the metabolic changes they’ve undergone. [Read More]
If it looks like a duck and quacks like a duck, so the adage goes, it must be a duck. But if the duck gets infected by a virus so that it no longer looks or quacks like one, is it still a duck? For a team led by researchers from The Ohio State University and the University of Michigan studying how virus infections cause significant metabolic changes in marine microbes, the answer is no. They refer to the infected microbial cells as virocells, a change in name which reflects the metabolic changes they’ve undergone. [Read More] A “bait and hook” single-cell genomic approach to bioprospecting. The Science One of the most vital pieces of equipment for fly fishing is a boxful of lures. Designed with feathers or wires to mimic an insect or a particular movement, each of these lures are the bait designed to attract specific catches. A similar technique… [Read More]
A “bait and hook” single-cell genomic approach to bioprospecting. The Science One of the most vital pieces of equipment for fly fishing is a boxful of lures. Designed with feathers or wires to mimic an insect or a particular movement, each of these lures are the bait designed to attract specific catches. A similar technique… [Read More] Over 40 percent of the cereal crop’s genes respond to drought stress. The Science Fields of drooping stalks and cracked earth are becoming common images in many regions due to more extreme weather events such as heat waves, droughts and floods. The planet’s resources are being stretched by a growing human population and increasing demand… [Read More]
Over 40 percent of the cereal crop’s genes respond to drought stress. The Science Fields of drooping stalks and cracked earth are becoming common images in many regions due to more extreme weather events such as heat waves, droughts and floods. The planet’s resources are being stretched by a growing human population and increasing demand… [Read More] For the first time, a team analyzes the transcriptomes of a lichen fungus and alga to understand their partnership more clearly. The Science The humble lichen is a superorganism: one being that is actually comprised of two (or more) participants. One is a fungus (usually belonging to the ascomycetes, one of the two main branches… [Read More]
For the first time, a team analyzes the transcriptomes of a lichen fungus and alga to understand their partnership more clearly. The Science The humble lichen is a superorganism: one being that is actually comprised of two (or more) participants. One is a fungus (usually belonging to the ascomycetes, one of the two main branches… [Read More] A better understanding of how poplar responds to endophyte associations with endophytes enables scientists to fine-tune their engineering efforts. [Read More]
A better understanding of how poplar responds to endophyte associations with endophytes enables scientists to fine-tune their engineering efforts. [Read More] A team has optimized a crucial part of CRISPR-Cas9 technology to enable improvements in microbial oil production. The Science CRISPR-Cas9 is a powerful, high-throughput gene-editing tool that can help scientists engineer organisms for bioenergy applications. Cas9 needs guide RNA to lead it to the correct sequence to snip — but not all guides are effective…. [Read More]
A team has optimized a crucial part of CRISPR-Cas9 technology to enable improvements in microbial oil production. The Science CRISPR-Cas9 is a powerful, high-throughput gene-editing tool that can help scientists engineer organisms for bioenergy applications. Cas9 needs guide RNA to lead it to the correct sequence to snip — but not all guides are effective…. [Read More] Nanohaloarchaeota cultures reveal they are symbionts and not free-living organisms. The Science Researchers employed multiple microbiology and ‘omics techniques to experimentally determine that Nanohaloarchaeota are symbionts, rather than free-living organisms as had been originally thought. The Impact The Antarctic lakes are a “treasure trove” of unknown microbes that play critical roles in environmental processes (related… [Read More]
Nanohaloarchaeota cultures reveal they are symbionts and not free-living organisms. The Science Researchers employed multiple microbiology and ‘omics techniques to experimentally determine that Nanohaloarchaeota are symbionts, rather than free-living organisms as had been originally thought. The Impact The Antarctic lakes are a “treasure trove” of unknown microbes that play critical roles in environmental processes (related… [Read More]