Finding the Fermenters
Building off JGI and KBase data resources, researchers developed an interactive and comprehensive database of fermentative microbes. [Read More]
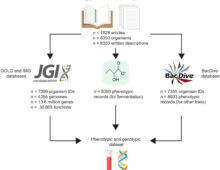 Building off JGI and KBase data resources, researchers developed an interactive and comprehensive database of fermentative microbes. [Read More]
Building off JGI and KBase data resources, researchers developed an interactive and comprehensive database of fermentative microbes. [Read More] JGI-enabled research shows eelgrass began colonizing oceans over 2.5 million years more recently than previously thought. [Read More]
JGI-enabled research shows eelgrass began colonizing oceans over 2.5 million years more recently than previously thought. [Read More] Scientists have discovered flagella in an unexpected place: hot spring-dwelling bacteria from the phylum Chloroflexota. Research shows that flagella were lost in other forms of Chloroflexota that adapted to marine environments hundreds of millions of years ago. [Read More]
Scientists have discovered flagella in an unexpected place: hot spring-dwelling bacteria from the phylum Chloroflexota. Research shows that flagella were lost in other forms of Chloroflexota that adapted to marine environments hundreds of millions of years ago. [Read More]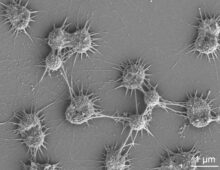 Recently, researchers used population genomics to find that while archaeal hitchhikers may often act as parasites, in other cases, they likely help their hosts. [Read More]
Recently, researchers used population genomics to find that while archaeal hitchhikers may often act as parasites, in other cases, they likely help their hosts. [Read More] Researchers at the JGI developed geNomad, a tool to quickly and accurately identify mobile genetic elements like plasmids and viruses. [Read More]
Researchers at the JGI developed geNomad, a tool to quickly and accurately identify mobile genetic elements like plasmids and viruses. [Read More] Building on existing virus-host prediction approaches, researchers have created a new program called iPHoP. It combines and evaluates multiple predictions to reliably match viruses with their archaea and bacteria hosts. [Read More]
Building on existing virus-host prediction approaches, researchers have created a new program called iPHoP. It combines and evaluates multiple predictions to reliably match viruses with their archaea and bacteria hosts. [Read More] Applying this method to the study of a particular fungi, researchers identified novel interactions between bacteria and the fungi. [Read More]
Applying this method to the study of a particular fungi, researchers identified novel interactions between bacteria and the fungi. [Read More] Microbial communities around hydrothermal vents survive in very hot, high-pressure and chemically-rich ecosystems. They hold clues for understanding how life thrives in extreme environments. [Read More]
Microbial communities around hydrothermal vents survive in very hot, high-pressure and chemically-rich ecosystems. They hold clues for understanding how life thrives in extreme environments. [Read More]![A photo of two sphagnum species: S. divinum (red) and S. angustifolium (green)]](https://jgi.doe.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Screen-Shot-2023-02-22-at-4.57.35-PM-220x170.png) Boggy peatlands, which hold much of the Earth’s carbon as well as material that can be converted to energy, are made up heavily of sphagnum mosses. [Read More]
Boggy peatlands, which hold much of the Earth’s carbon as well as material that can be converted to energy, are made up heavily of sphagnum mosses. [Read More]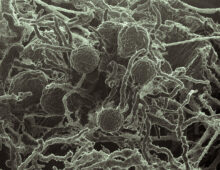 A new study offers the first irrefutable proof that anaerobic fungi — the kind living in the stomachs of livestock — can deconstruct lignin in the absence of oxygen. [Read More]
A new study offers the first irrefutable proof that anaerobic fungi — the kind living in the stomachs of livestock — can deconstruct lignin in the absence of oxygen. [Read More]