The JGI Safety and Wellness Team is a group of employees who focus on promoting safety and wellness in the workplace and at home. Formerly known as the Safety Culture Group, each member is an advocate of safety and ergonomics and engages in activities that promote healthy living, wellness, and sustainability. As our surrounding environments…
Modeling Microbial Networks in an Oxygen Minimum Zone
UBC team develops predictive marine microbiome math model. The Science With help from two DOE national user facilities, a team at the University of British Columbia (UBC) has developed a math model that could help researchers and policy makers track the impact of climate change on the microbial networks that drive the world’s marine ecosystems….
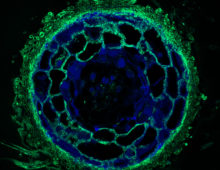
The Poplar Genome at 10
The poplar genome paper has been cited some 1,900 times since its 2006 publication in Science, but that’s not the only way to measure its impact.
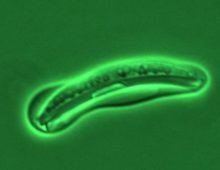
Microbial dark matter in Science News
“In one of her first projects, Tanja Woyke analyzed the bacterial community huddled inside a worm that lives in the Mediterranean Sea. Woyke, a microbiologist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Joint Genome Institute in Walnut Creek, Calif., and colleagues published the report in Nature in 2006. It was two years in the making.” Our…
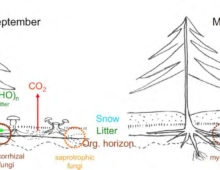
How Fungi Help Trees Tolerate Drought
Genome of world’s most common fungal symbiont sheds light on drought resistance role The mutualistic relationship between tree roots and ectomycorrhizal (ECM) fungi has been shaping forest ecosystems since their inception. ECM fungi are key players supporting the growth, health and stress tolerance of forest trees globally, such as oak, pine, spruce, birch and beech,…
10 New Projects to be Supported Under Joint DOE User Facility Initiative
The U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute (DOE JGI) and the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL) have accepted 10 projects submitted during the 2017 call for proposals for their joint “Facilities Integrating Collaborations for User Science” (FICUS) initiative. These new research projects all involve collaboration between two user facilities that are stewarded by the DOE Office…
Microbial Metabolism Impacts Sustainability of Fracking Efforts
Team finds surface microbes are colonizing the deep subsurface. The Science Through a collaborative science program involving two DOE national user facilities, DOE-supported researchers have been able to reconstruct microbial genomes for the first time from shale formations that are being drilled to extract natural gas. Coupled with microbial metabolic information, the data shed light…
Unveiled: Earth’s Viral Diversity
Environmental datasets help researchers double the number of microbial phyla known to be infected by viruses. The number of microbes in, on, and around the planet – on the order of a nonillion, or 1030 – is estimated to outnumber the stars in the Milky Way. Microbes are known to play crucial roles in regulating…
Expanding the Stable of Workhorse Yeasts
New genome sequences target next generation of yeasts with improved biotech uses The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae was a part of human civilization before history was recorded. It is essential for making bread, beer and wine, and it is ubiquitous. It is not, however, typical of the more than 1,500 yeast species found around the world….
Identifying the Microbial Culprits Initiating Oceanic Nitrogen Loss
Novel lineages of SAR11 clade reveal adaptations to oxygen-poor ocean zones. The Science Oxygen minimum zones (OMZs) extend over about 8 percent of the oceanic surface area, but account for up to 50 percent of the total loss of bioavailable nitrogen and thus play an important role in regulating the ocean’s productivity by substantially impacting…