Analysis of haloarchaeal metagenomes broadens understanding of Antarctic biogeography.
The Science
Haloarchaea flourish in hypersaline environments, and researchers are interested in learning how these microbes have learned to adapt from marine to hypersaline conditions by studying the microbial communities in Antarctic lakes, some of which have salinities 10 times that of seawater. To shed light on the global biogeography in the haloarchaeal gene pool, a team led by University of New South Wales (UNSW)-Sydney professor Rick Cavicchioli compared two strains of haloarchaea from different Antarctic lakes. To assess the genomic variation in haloarchaea, they also characterized metagenomes (collections of partial genomes) from six hypersaline Antarctic lakes.
The Impact
By collecting and sequencing dominant haloarchaeal sequences from six hypersaline lakes, researchers focused on understanding the genomic variation in haloarchaea across East Antarctica. The implications of the current study are important both to understanding genomic variation in Antarctic lake environments, and also to characterize regional and global biogeography of haloarchaea and the structure and extent of the Antarctic microbial pan-genome. Since these microbes thrive under extreme temperature and salinity conditions, understanding their adaptations offers insights into microbial evolution, as well as how Antarctic microbial communities contribute to global biogeochemical cycles, and possibly cold-temperature enzymes for biotechnological use.
Summary
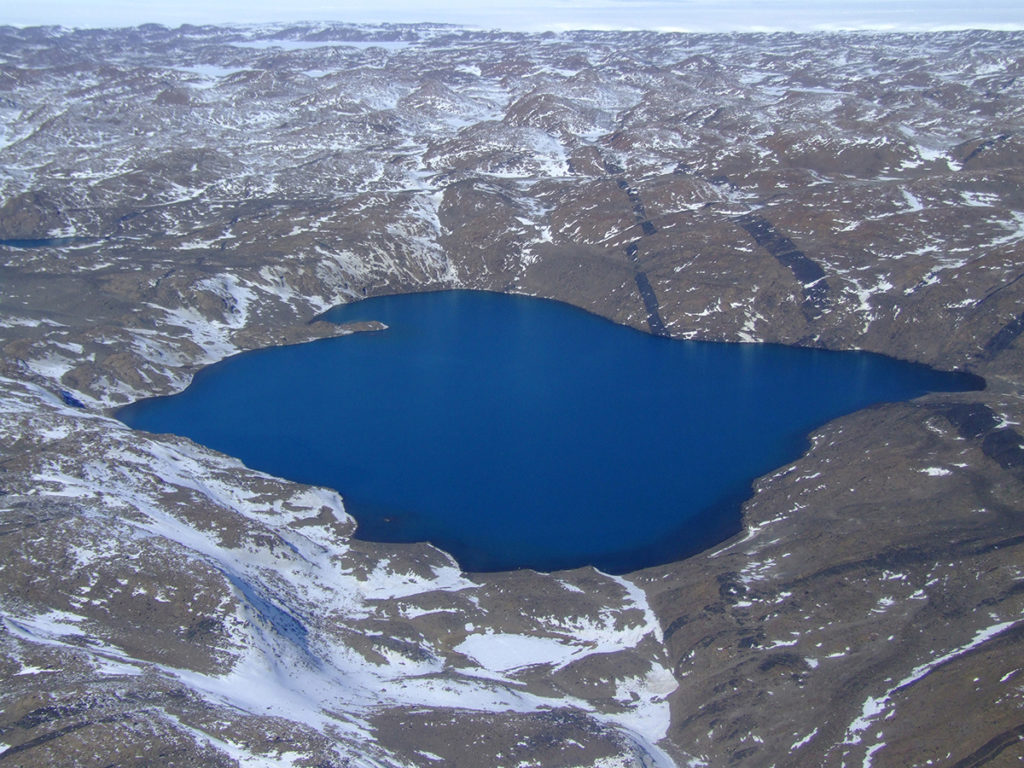
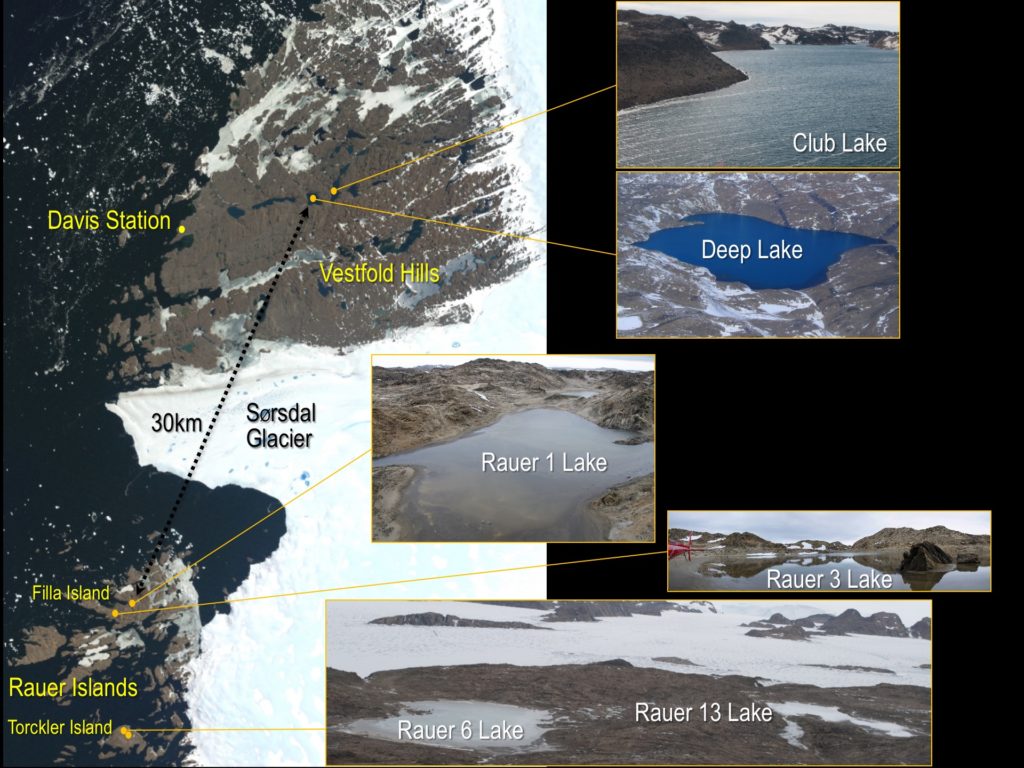
Conditions such as extreme cold, high levels of salinity and the sheer distance from other parts of the world have kept microbial populations on Antarctica distinct and unique. In collaboration with the DOE Joint Genome Institute, a DOE Office of Science User Facility, microbial ecologist Rick Cavicchioli and his team have been studying the haloarchaea that thrive in the very salty waters of Deep Lake to better understand how they’ve adapted to these conditions, information that could have biotechnological applications. The work has been enabled through the JGI Community Science Program (CSP).
Cavicchioli and his team compared two strains of Halorubrum lacusprofundi from Deep Lake and Rauer 1 Lake, one of the lakes in the nearby Rauer Islands. Additionally, they compared metagenome data generated from samples collected at four Rauer lakes to assess population level genomic variation. The genome and metagenome data are available through JGI’s Integrated Microbial Genomes & Microbiomes (IMG/M) platform.
These data allowed researchers to define a haloarchaea “pan-genome.” Described as the total pool of genetic material comprised by all members of a species, the pan-genome of haloarchaea contains the parts of the genome shared across all haloarchaea, along with the pool of genes considered the flexible genome content that was likely acquired due to gene transfer events. Such events can occur in response to viral infections and are important for virus-host interactions. Analysis of strain variation showed that haloarchaea generally have a primary replicon (chromosome) that is highly conserved and secondary replicons that are highly variable but organized in blocks, or “islands,” suggesting that the acquisition via horizontal gene transfer mechanisms involved significant sized pieces. Interestingly, much of the strain variation appeared related to defense against viruses. Experiments infecting H. lacusprofundi with an Antarctic halovirus demonstrated differences in resistance between two strains. But perhaps the largest implication of this study is the evidence that H. litchfieldiae and H. lacusprofundi are found across all six lakes, suggesting that these species are endemic to Antarctica and distinct from other hypersaline environments.
Contacts:
BER Contact
Daniel Drell, Ph.D.
Program Manager
Biological Systems Sciences Division
Office of Biological and Environmental Research
Office of Science
US Department of Energy
daniel.drell@science.doe.gov
PI Contact
Rick Cavicchioli
School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences
UNSW Sydney
r.cavicchioli@unsw.edu.au
Funding:
This work was supported by the Australian Research Council (DP150100244) and the Australian Antarctic Science program (project 4031). The work conducted by the US Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute, a DOE Office of Science User Facility, is supported by the Office of Science of the US Department of Energy under contract no. DE-AC02-05CH11231. S.E. was supported by the EMBO Long-Term Fellowship ALTF 188–2014, which is co- funded by the European Commission (EMBOCOFUND2012, GA-2012-600394) and supported by Marie Curie Actions.
Publication:
- Tschitschko B et al. Genomic variation and biogeography of Antarctic haloarchaea. 2018. Microbiome 2018 Jun 20;6(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0495-3.
Related Links:
-
- Nature Research Microbiology Community blog post: “Antarctic haloarchaea – a unique Microbiome”
- JGI Community Science Program
- Approved FY15 CSP Proposal: Baselining Antarctic microbial communities
- JGI News Release: “Cold, Salty and Promiscuous—Gene-shuffling Microbes Dominate Antarctica’s Deep Lake”
Byline: Massie Santos Ballon