Novel mechanism in bacterial-fungal symbiosis could have biodiesel production applications
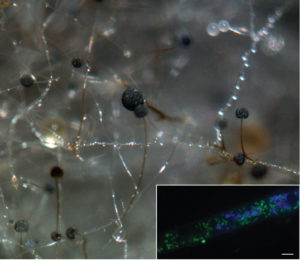
Hyphae and asexual sporangia of Rhizopus microsporus (photo by Stephen Mondo). Inset shows a hypha with YFP-labeled Burkholderia endobacteria in green and DAPI-stained fungal nuclei in blue; scale bar, 5 um (photo by Olga Lastovetsky)
The Science
To answer the challenge of producing renewable, sustainable alternative fuels, researchers aren’t just looking at developing candidate bioenergy crops but are also reviewing other natural sources of energy-dense oils such as fungi. To learn more about how bacteria interact with fungi in a symbiotic relationship to support the biochemistries that could contribute to the development of alternate fuel sources, Cornell and DOE JGI researchers used a model bacterial-fungal system to reveal the mechanism for lipid production in oil-producing or oleaginous fungi.
The Impact
Fungi are most often found in complex communities that include bacteria among other members. Understanding how fungal-bacterial interactions influence lipid production in Mucoromycotina fungi offers insights into how these fungi might be harnessed for biodiesel production.
Summary
The widespread use of antimicrobials has led to the perception that fungi and bacteria are antagonists, but this is not always true. In a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences paper published online December 12, 2016, researchers at Cornell University and the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute (DOE JGI), a national user facility, reported on the mechanisms influencing the mutualistic relationship between the fungal plant pathogen Rhizopus microsporus and a Burkholderia endosymbiont. Rhizopus is a plant pathogen of crops including rice, sunflower, and maize, and it relies on the toxin produced by the endosymbiont bacteria. Their symbiotic relationship was discovered in 2005, and researchers expect more examples of fungal-bacterial mutualisms to be found now that they are being actively sought out. The Cornell team cultivated the fungi and isolated the endobacteria while the DOE JGI team sequenced, assembled and annotated the genomes of the host and non-host genomes as part of the DOE JGI’s 1000 Fungal Genomes project and other DOE JGI Community Science Projects. The results indicate that the transition between symbiosis and antagonism between the bacteria and their fungal host is driven by a novel mechanism involving fungal lipid metabolism. “When lipid metabolism in the fungus is triggered and phosphatidic acid (PA)-producing enzymes are activated, the fungus and bacteria act as mutualists. When the PA-producing enzymes are inhibited, the bacteria and fungi act as antagonists,” said Cornell’s Teresa Pawlowska and her graduate student Olga Lastovetsky. This work highlights the complicated nature of fungal-bacterial relationships that can oscillate between mutualistic and antagonistic. The work also lends bioenergy researchers insight into lipid metabolism in an oil-producing fungus, and how this can influence the nature of their interactions.
Contacts
Daniel Drell, Ph.D.
Program Manager
Biological Systems Sciences Division
Office of Biological and Environmental Research
Office of Science, US Department of Energy
daniel.drell@science.doe.gov
Igor Grigoriev
Fungal Genomics Head
DOE Joint Genome Institute
ivgrigoriev@lbl.gov
Funding
- DOE Office of Science
- National Science Foundation
Publications
- Lastovetsky OA et al. Lipid metabolic changes in an early divergent fungus govern the establishment of a mutualistic symbiosis with endobacteria. Proc Nat Sci Acad. 2016 Dec 12. doi:10.1073/pnas.1615148113 [Epub ahead online]