DOE-funded researchers develop a new process for annotating cellulose-degrading enzymes.
The Science:
Researchers at two Department of Energy-funded Scientific User Facilities collaborated with one of three Bioenergy Research Centers to develop and analyze high-resolution crystal structures of an enzyme from the cellulose-degrading GH55 family. They then went further and were able to apply a variety of techniques that resulted in the “most complete functional mapping of an entire GH family available to date.”
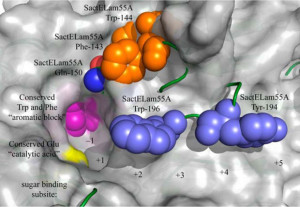
Combining the scientific resources of two DOE Office of Science User Facilities, the Advanced Photon Source and the DOE Joint Genome Institute, researchers were able to examine the dynamic motion of several residues surrounding the active site of the substrate-bound structure of SacteLam55A, a glycoside hydrolase (GH) enzyme. (Image from Bianchetti CM et al, J Biol Chem. 2015 May 8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.623579.)
The Impact:
Members of the GH55 enzyme family are known for their ability to break down cellulose and thus are of interest to bioenergy researchers working on advancing large-scale biofuels production. The approach described in this study could speed up the process of studying cellulose-degrading enzymes by allowing researchers to study entire families at once.
Summary
Many of the microbial and metagenome projects conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute (DOE JGI), a DOE Office of Science user facility managed by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, focus on microbial communities in the guts of insects and animals because of their roles in breaking down the plant mass consumed by these hosts for energy. When DOE JGI researchers published the cow rumen metagenome in Science, they added nearly 30,000 candidate cellulose-degrading genes that encode carbohydrate-active enzymes to the (CAZymes) database from that one project alone.
The process of functionally annotating each one of these genes, however, can be time-consuming. For enzymes in the GH55 family of cellulose-degrading genes, for example, much of the previous work has been carried out on fungi. For example, the structure of the protein PcLam55A was derived using the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium, which had been sequenced by the DOE JGI.
In a study published May 8, 2015 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, a team including researchers from the DOE JGI and the DOE-funded Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center characterized the structure and function of another GH55 protein – SacteLam55A. The gene SACTE_4363 encodes this protein and was isolated from the microbe SirexAA-E in the gut of the pinewood-boring wasp Sirex noctilio. The gene was found when the microbe was grown on cellobiose, xylan, and pretreated switchgrass samples, suggesting it has cellulolytic properties.
To determine the gene’s structure, researchers relied on diffraction data collected at the Advanced Photon Source, a DOE user facility at Argonne National Laboratory to develop high-resolution crystal structures. Through assays, and techniques such as gene synthesis and cell-free protein translation, the team was also able to characterize the biochemistry and structure of the GH55 family.
“The combination of gene synthesis, cell-free translation and assays using a diagnostic panel of substrates across the entire GH55 represents, to our knowledge, the most complete functional mapping of an entire GH family available to date,” the team reported. The collaboration of two DOE User Facilities with a DOE Bioenergy Research Center that enabled this research, combining disparate technologies, will advance the understanding of cellulose structure and function to a depth beyond the capabilities of any one Facility.
Contact
Sam Deutsch
DOE Joint Genome Institute
sdeutsch@lbl.gov
Funding
- U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science
- University of Wisconsin
- Michigan Economic Development Corporation
- Michigan Technology Tri-Corridor
Publication
- Bianchetti CM et al. Active site and laminarin binding in glycoside hydrolase family 55. J Biol Chem. 2015 May 8: 290, 11819-11832. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.623579.