DOE JGI Interns Share Their Summer Experiences
In 2015, the JGI hosted 10 interns who spent the summer crunching genomic data at a computer, working at the lab bench, and even spending time out in the field. [Read More]
 In 2015, the JGI hosted 10 interns who spent the summer crunching genomic data at a computer, working at the lab bench, and even spending time out in the field. [Read More]
In 2015, the JGI hosted 10 interns who spent the summer crunching genomic data at a computer, working at the lab bench, and even spending time out in the field. [Read More]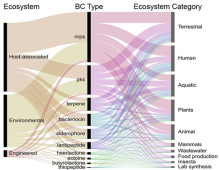 IMG-ABC allows researchers to link sequencing data and the search for novel biosynthetic gene pathways. The Science: The wealth of genomic and metagenomic datasets for microbes, particularly from previously unstudied environments, within the Integrated Microbial Genomes (IMG) system is being applied in a new public database to the search for novel secondary metabolites that could… [Read More]
IMG-ABC allows researchers to link sequencing data and the search for novel biosynthetic gene pathways. The Science: The wealth of genomic and metagenomic datasets for microbes, particularly from previously unstudied environments, within the Integrated Microbial Genomes (IMG) system is being applied in a new public database to the search for novel secondary metabolites that could… [Read More] Identifying pathways in algae that produce oil without killing them While most people might know some algae as “pond scum,” to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), they are tiny organisms that could provide a source of sustainable fuels. Like plants, they can convert light into energy-rich chemical compounds; unlike plants, they require less space… [Read More]
Identifying pathways in algae that produce oil without killing them While most people might know some algae as “pond scum,” to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), they are tiny organisms that could provide a source of sustainable fuels. Like plants, they can convert light into energy-rich chemical compounds; unlike plants, they require less space… [Read More]