
On July 6, scientists from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and other institutions shared their works-in-progress with 86 participants in an online workshop to harness deep learning for metagenomic data.
Metagenomic data, or DNA sequencing data gathered from whole samples rather than single cells or isolated strains, is easy to generate, but difficult to assemble and interpret. The workshop aimed to showcase how researchers are utilizing deep learning to automatically generate insights from metagenomic data.
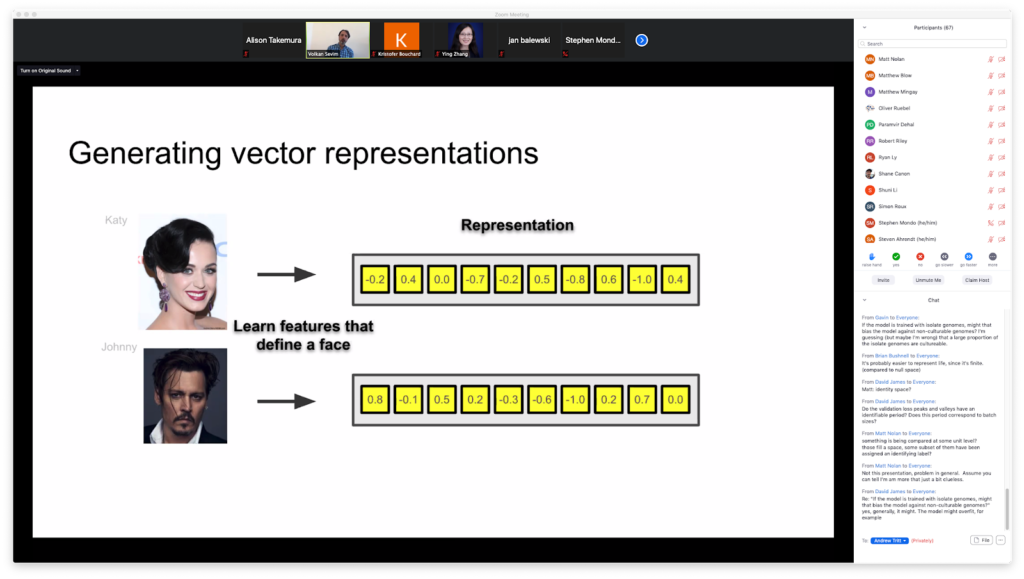
In deep learning, a branch of machine learning, data is passed through algorithms organized into multiple interconnected layers. The architecture of these algorithms, inspired by communication networks found in nature, allows machines to “learn” features. State of the art algorithms can perform astonishing degrees of feature recognition: for example, a camera’s ability to recognize your face and distinguish it from your friend’s. Biologists aim to capitalize on these kinds of abilities by applying them to sequencing data.

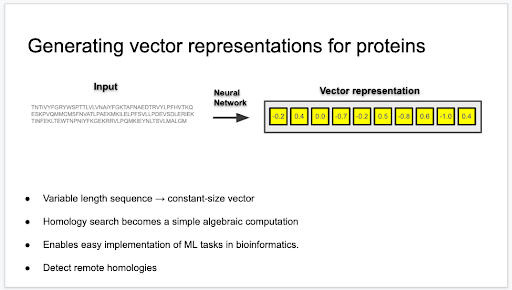
At the workshop, Volkan Sevim, a computational biologist at the US Department of Energy (DOE) Joint Genome Institute (JGI), presented on generating vector representations of proteins in order to conduct more efficient protein sequence alignments. He also aims to detect structural similarities in proteins that low sequence identity may belie. The technology he’s using is magical; transform any length of amino acid sequence into a smaller, constant-length vector using deep learning. Vector representations allow homology searches between proteins to become much simpler; instead of aligning sequences with popular, but computationally costly approaches such as BLAST and hidden Markov models (HMMs), “You just compute the distance between two vectors,” said Sevim.
While there are alignment-free methods for nucleotide searches, such as Mash and BBsketch, whose lead developer is JGI software developer Brian Bushnell, no alignment-free tool exists for proteins. (And while Mash and BBsketch can be used on nucleotide sequences, they’re not as reliable on amino acid sequences.) Sevim is currently using HMM profiles of protein domains from the pfam database to test the efficacy of a particular kind of deep learning algorithm — a convolutional neural network, called ResNet 34 — in order to vectorize protein sequences.
Sevim is part of the JGI Genome R&D Group and is one of more than 100 scientists and systems engineers involved in computational work at the JGI. Sevim’s work is part of an ongoing effort to build greater collaboration between JGI and scientists in the Computational Resources Division (CRD), in order to create more useful tools for the bioinformatics community.
Other work presented at the workshop included how to use deep learning to predict protein function (Héctor García Martin of Berkeley Lab’s Biological Systems and Engineering), to assign microbial taxa (Andrew Tritt of CRD and, independently, Ying Zhang of the University of Rhode Island), and to bin metagenomic contigs (inferred chromosomal sequences in mixed-genome samples) with a new tool called MetaGNN (Prashant Pandey of CRD).
The workshop was organized by Kristofer Bouchard, neuro- and data scientist in Biological Systems and Engineering / Computing Resources Division (BSE/CRD).
By Alison F. Takemura