For submission of materials in 96-well plate format, the JGI requires that investigators adhere to the guidelines outlined below in addition to the material-specific sample requirements described on our website.
The following library types are supported in plate format:
DNA:
- Illumina fragment libraries (typically used for microbial and fungal minimal drafts, metagenomes, resequencing)
- Nextera fragment libraries (typically used for single cell and single particle sort projects)
RNA:
- PolyA-selected libraries
- rRNA-depleted libraries
For all other library types, please ship your samples in tubes. If you are unsure of the correct format, please discuss with your Project Manager.
Sample Preparation
- If you are shipping 22 or more samples at one time from the products listed above, you should submit in 96-well plate format.
- A maximum of 92 samples per plate may be submitted.
- We recommend sending DNA samples in low EDTA TE buffer (molecular biology grade, DNase/RNase/protease-free, such as this one from VWR), and RNA samples in DNase-treated and nuclease-free water, where they are most stable.
- You must assess the quality of at least 10% of samples prior to submission. JGI’s recommended protocols are below.
Genomic DNA QC protocol | Total RNA QC protocol
Plate Preparation
- We require the use of the prelableled, barcoded plates provided by the JGI.
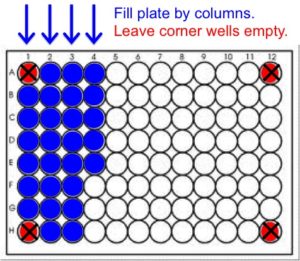
- Leave the corner wells (A1, A12, H1 and H12) EMPTY.
- Fill the plate by column, placing the first sample in well B1 (Column 1 B-G, then Column 2 A-H, Column 3 A-H, etc.). See diagram below.
- The mass should be consistent across all samples in the plate and within the ranges below. If you are unable to provide sufficient mass, please contact your Project Manager, as alternate protocols may be available (though typically at much lower throughput).
- Leave unused wells empty.
- After placing samples in the plate, seal with the new sealer contained within the shipment.
| Library type | Requested mass (ng)* | Volume range (ul) | Concentration range (ng/ul) | DNAse treatment required | Minimum # samples per plate | Maximum # samples per plate |
| Illumina fragment (400 bp) | 500 | 25-150 | 10-1000 | No | 22 | 92 |
| Nextera fragment |
10 | 25-150 | 0.2-1000 | No | 22 | 92 |
Plate Naming
- Plate name must be unique and descriptive, and <21 characters in length.
- “Plate Label” is the field in the metadata submission tool in which you will enter this information.
- Prior to shipment, confirm that the plate label information submitted with the metadata matches the physical label on the plate.
- Mismatched or improperly labeled materials will be returned to the shipper.
Examples:
- 504675_RNA.1
- Smith_DNA300_5
If you are having trouble determining a unique name for your plate, please consult your Project Manager.
Plate Processing
- JGI’s library construction protocols are optimized for use on full plates of samples. Samples from your plate may be combined with samples from other plates, at JGI’s discretion.
Last update: 4/20/23