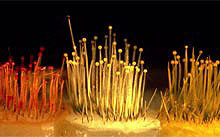
Members of the phylum Chytridiomycota are unique among the fungi in possessing flagellated zoospores. Furthermore, the anaerobic chytrid fungi represent a unique order (Neocallismasticales) within the chytrids that possess hydrogenosomes (hydrogen- and ATP-producing organelles), lack mitochondria, and grow as commensal organisms in the gut of a variety of herbivores. These obligate anaerobic chytrid symbionts play…
Why Sequence Phytophthora capsici?
Phytophthora capsici is a devastating pathogen of vegetable crops such as cucurbits (squashes, pumpkins, etc.), tomatoes, and peppers. A pathogen of national economic importance, it has recently expanded its host range to include legumes. Sequencing P. capsici will provide vegetable and Phytophthora investigators nationwide with gene models for comprehensive functional genomic studies of natural populations…
Why Sequence Phycomyces blakesleeanus?
The zygomycete fungus Phycomyces blakesleeanus has been investigated over several decades for the variety and sensitivity of its responses to light, particularly the phototropism of the giant fruiting body, the sporangiophore. Other light responses investigated in detail are the regulation of sporangiophore development and the regulation of the biosynthesis of beta-carotene. In addition, the Phycomyces…
Why Sequence a Porcelain Crab?
How animals respond to climate change will depend on their thermal habitats and their thermal phenotypes. The thermal phenotype of an organism (heat and cold tolerance, thermal range, and thermal plasticity) is an essential feature of how the organism performs across thermal environments and in response to thermal stress. Porcelain crabs are of interest in…
Why Sequence Amphipod Crustaceans?
This project comprises preliminary directed genome and EST sequencing of two species of amphipod crustaceans. Parhyale hawaiensis is becoming an established “new model” organism for developmental studies within the arthropods. Jassa slatteryi is another related amphipod crustacean found to have an unusually small genome relative to other amphipods. These species have phylogenetically strategic positions with…
Why Sequence the Low-Light Strain of Ostreococcus?
Ostreococcus belongs to the Prasinophyceae, an early-diverging class within the green plant lineage, and is reported as a globally abundant picoeukaryotic group (tiny algae) throughout the oceanic euphotic zone (the top of the water column, where green plants live). The most striking feature of O. tauri and related species is their minimal cellular organization: a…
Why Sequence the California Mussel?
Sequencing the mussel Mytilus californianus will have direct impacts on multiple DOE missions. The fields of ecotoxicology and environmental remediation stand to benefit from their ability to sequester toxins. Mussels are frequently used as sentinel organisms for monitoring the accumulation of pollutants in marine ecosystems. The measurement of chemicals in mussel tissue provides an estimate…
Why Sequence Mycosphaerella fijiensis?
Mycosphaerella fijiensis, the causal agent of the devastating leaf streak disease (commonly called Black Sigatoka) in bananas, requires the highest annual fungicide application of all pathogens globally (more than $2.5 billion worth). This pathogen is of urgent importance, as banana production relies heavily on massive use of a fungicide that is under critical public review…
Why Sequence Cichlid Fish?
The sequencing of several Lake Malawi cichlid fish will contribute to major advances in our understanding of evolution in Lake Malawi cichlids. The lake is an evolutionary treasure trove in East Africa, home to more species of freshwater fish than all of Europe and North America combined. In part because cichlids are commonly used in…
Why Sequence Poplar Leaf Rust?
The Populus (poplar tree) genome has been publicly released by the JGI, and the genomes of its symbiotic fungal associates Laccaria bicolor and Glomus intraradices are near completion. As part of the development of a broader community-based Populus genomics resource, and as a means of conducting informative comparative genomics among fungi, JGI will be sequencing…