Terpenoids are one of five families of hydrocarbons produced by fungi that are of interest to bioenergy researchers either as biofuels or biofuel precursors. Terpenoids such as hydrogenated bisabolene have been suggested as a viable alternative to D2 and biodiesel fuels. These compounds hold promise as a renewable source of microbially synthesized biofuels. To remedy…
Further Studies in Poplar Rust Fungal Genomics
Rust fungi (Pucciniales) are among the most important pathogens of many plants and trees of agricultural and ecological importance including DOE JGI Plant Flagship Genomes such as soybean, sorghum and poplar. The fungi are also known to have the most complex lifecycles among fungi. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that control interactions between plants and rust…
Effects on mutations on Aspergillus genomes
Aspergilli fungi are widely used in the biotechnology industry, and are emerging as the best model systems for fungal comparative genomics. However, the evolution of Aspergilli is still understudied. The production of these bioenergy bioenzymes is regulated by general regulatory mechanisms of carbon catabolism, and Aspergillus species have become established model organisms for the study…
Expanding grass genome comparators
The panicoid clade of grasses form the dominant component of grassland ecosystems around the world. They include some of the most photosynthetically productive crops in the world and five species have been selected by the DOE JGI as “flagship genomes,” primarily based on the potential of the species to serve as biofuels crops: sorghum (Sorghum…
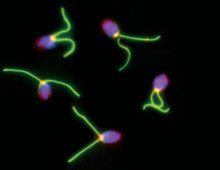
Fungal-bacterial symbioses with Populus
Bacteria and fungi are known to interact with plants and contribute to ecosystem health and productivity, defining the plant microbiome. Recent studies indicate that some fungal-bacterial symbioses may date back over 400 million years and may be important in driving the formation of soil and rhizosphere communities. This project focuses on a diversity of fungi…
Getting a Jump on Plant-Fungal Interactions
Transposable elements in a genome could make plant pathogens more flexible with their hosts. The Science: Researchers examined a correlation between fungal plant pathogens and the abundance of transposable elements in their genomes. They looked at the mechanisms of transposable elements in symbionts that are similar to those in pathogens. The Impact: Fungal plant pathogens may…
Gene expression analyses of Populus crosses
Populus is one of DOE JGI’s Flagship Plant Genome species and is of special interest as a biofuels feedstock. It was selected as the model forest species for genome sequencing due to its modest genome size, rapid growth, relative ease of experimental manipulation and range of available genetic tools. As such, Populus trichocarpa was the…
Carbon studies in Northern California
The global terrestrial carbon reservoir is primarily distributed among grasslands, forests and cultivated farms. While the majority of fixed carbon is stored in vegetation in forests, most fixed carbon in grasslands is stored in soil. Thus, it is critical to understand the carbon cycling in grassland soil. One challenge climate researchers face is making accurate…
A Decade of Improvements on the Reference Green Alga Genome
Since the generation of the first draft sequence, DOE JGI researchers have been improving a key algal genome. The Science: The high-quality genome sequence of the tiny single-celled alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has proved useful for researchers studying photosynthesis and cell motility. The Impact: In the decade since researchers initiated plans to sequence and now annotate…
In Memoriam: Falk Warnecke
Falk Warnecke was a postdoctoral fellow at the DOE JGI’s Microbial Ecology Program from March 2005 until June 2009. Among the publications that resulted from his work here, he was first author on the termite hindgut metagenome paper that appeared in Nature. Warnecke died on July 15, 2014 at the age of 42. Within a…