Researchers isolated and sequenced four species of Hydrogenobaculum.
Sinking SOS levels lead to reduced salt tolerance
The Food and Agriculture Organization reported that salt levels in the soil is reducing the world’s agricultural lands at the rate of one percent a year. Concerns over feeding a growing global population with limited arable land have led to interest in developing salt-tolerant crops for food and fuel Found on the seashores of eastern…
Metagenomic study of methane in marine microbial communities
Methane is one of the most potent greenhouse gases and previous studies suggested that it is removed from the atmosphere through aerobic and anaerobic processes with the help of bacteria and archaea. Recent evidence suggests, however, that methane can be removed through other pathways involving as-yet unidentified microbes. To learn more about these pathways and…
“There’s a war going on in our oceans, a huge war, and we never even saw it,” said Stephen Giovannoni, a professor of microbiology at Oregon State University. “This is an important piece of the puzzle in how carbon is stored or released in the sea.” Read the full story at Futurity
Genome evolution with the help of plasmid gene pools
Plasmids are DNA molecules that can replicate independently of chromosomal DNA in a cell. This ability allows them to “collect” and move genes, such as through lateral gene transfer, and is a factor that allows prokaryotic genomes to evolve over time. To understand the depth and breadth of this plasmid gene pool in prokaryotes, researchers…
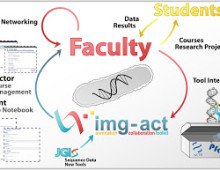
Student tools for hands-on genomics and bioinformatics lessons
Driven in part by the increased emphasis to give life sciences students hands-on experience in “real research,” the DOE Joint Genome Institute’s Genomics and Bioinformatics Education Program developed a series of educational modules for undergraduate programs to explore and annotate publicly available microbial genome datasets. Known collectively as the Integrated Microbial Genomes Annotation Collaboration Toolkit…
Lessons learned from comparing Cochliobolus fungi
Cochliobolus fungi are cereal grain pathogens in the Dothideomycetes class, and many species are known to infect crops such as corn, rice, barley, wheat and oats, causing severe losses at harvest time and to biomass feedstocks for biofuels. In a study published January 24, 2013 in Plos Genetics, one in a series of publications concerning…
DOE JGI team recognized for cotton genome project
“As part of the recent Plant and Animal Genomic Conference held in San Diego, Dr. Don Jones of Cotton Incorporated presented the 2012 Cotton Biotechnology Award to five outstanding researchers that were instrumental in mapping the cotton genome. The diverse and talented team, composed of Dr. Andrew Paterson, Dr. Jonathan Wendel, Mr. Jeremy Schmutz, Dr. Dan Peterson, and Dr. Dan Rokhsar led the collaborative…
A fungal pathogen with a “genetically flexible” genome
In 2012, the damp winter threatened the wheat harvest in the state of Kansas, the nation’s single largest producer of the grain and wheat prices rose by 10 percent as a result. Diseases such as tan spot caused by the fungus Pyrenophoratritici-repentis (Ptr) factored into the reduced wheat harvests. In North Dakota, which ranks second…
DOE JGI Science Highlight: Benefits of “diversity-driven genome sequencing” in CyanoGEBA
Despite their miniscule size, cyanobacteria play significant roles in the global carbon and nitrogen cycles. Researchers are also looking at utilizing them for biofuel and biotechnology applications. In an effort to learn more about the diverse strains in this phylum, DOE Joint Genome Institute scientist Cheryl Kerfeldis leading an effort called CyanoGEBAto increase the number…