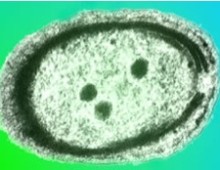
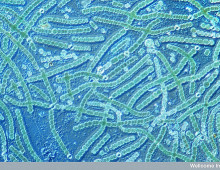
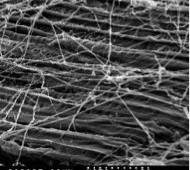
Yellowstone yields novel achaeon and candidate Archaea phylum
When a third branch to the Tree of Life was proposed several decades ago, the evidence used to support the need to recognize the kingdom Archaea came in the form of two divisions of organisms that could not be categorized as Eukaryotes or Bacteria. Since then, several more archaeal phyla have been recognized, many of them… [Read More]