Gain access to omics technologies generating community data at zero cost — submit a proposal.
Video file
The JGI offers access to deep expertise and a broad toolset.
The JGI at a Glance
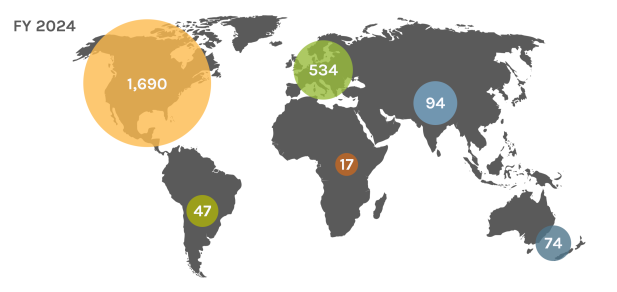
Global Users
Each year, the JGI serves over 2,000 users — researchers with accepted project proposals — at all career stages.
A Diversity of Capabilities
With an accepted proposal, JGI Users gain access to deep expertise and a broad toolset.
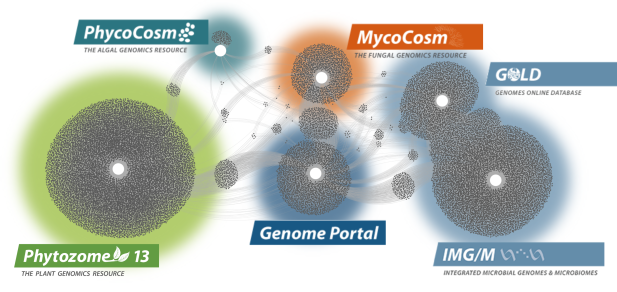
Data Portals
We generate and provide access to data that support interdisciplinary work on a broad variety of organisms. Each dot in these networks shows a publication that mentions a given data portal, with work that cross-references multiple portals in between respective hubs.
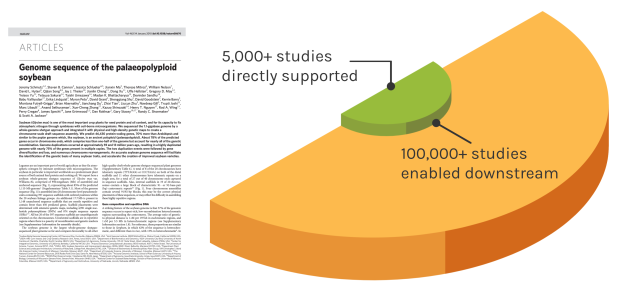
Foundational Work
JGI’s scientific contributions reverberates over time to enable many discoveries. The Soybean genome shown is one example — since the original reference genome, the entire project has directly impacted over 5,000 unique studies. These works have gone on to influence over 100,000 further studies.

JGI announces 2025 New Investigator portfolio
This year, the JGI has accepted novel research projects from a record 30 PIs who have not led previously accepted proposals.

With a new methodology, scientists are now getting more complete genomic results from single cells
PTA is a refined capability that is desirable in the microbiome field due to its high recovery of single-cell genomes. Offering this tool establishes the JGI as a leader in single-cell genomic amplification at a large scale.

JGI releases 2024 Progress Report
For the fiscal year 2024, a record number of researchers — 2,475 users — had active proposals with the JGI; more than 15,000 others have accessed and utilized the data we either generate or make available.




